Table of Contents
What Are Bunions?
What Are The Causes of Bunions?
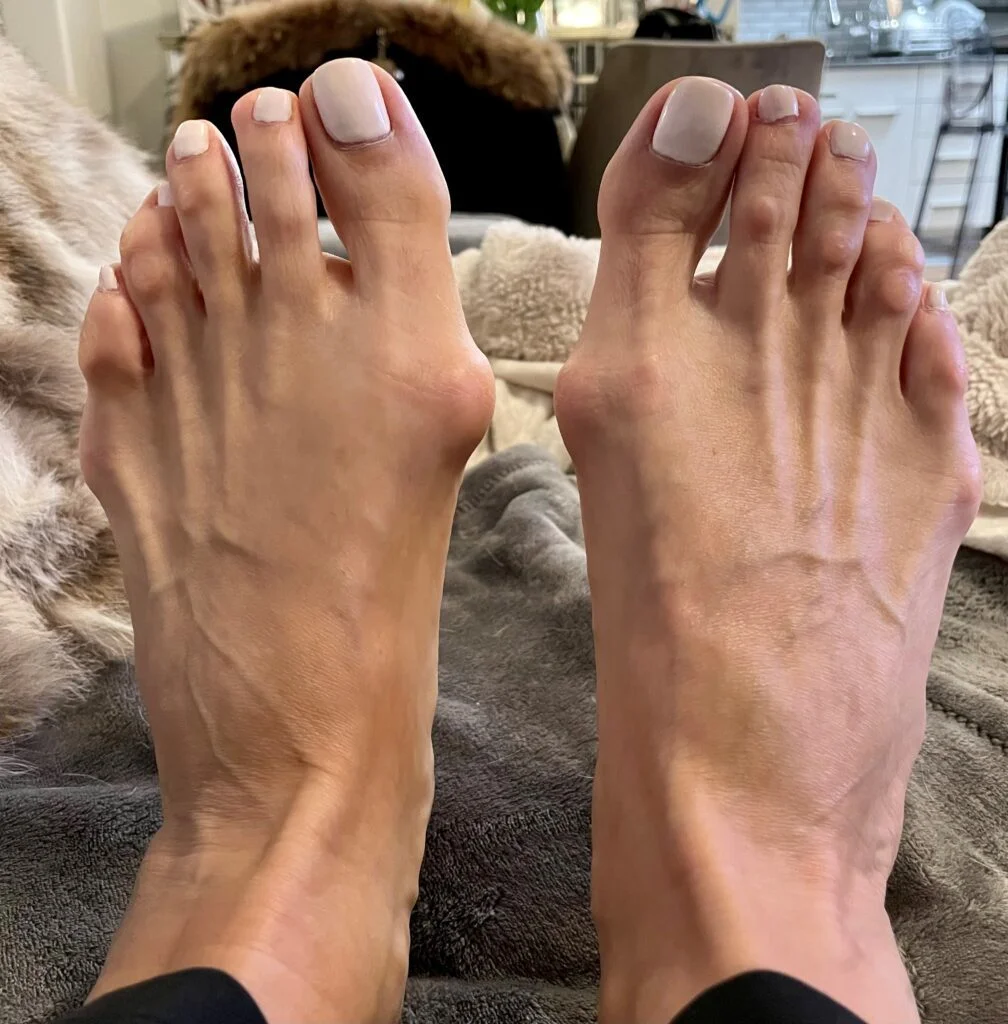
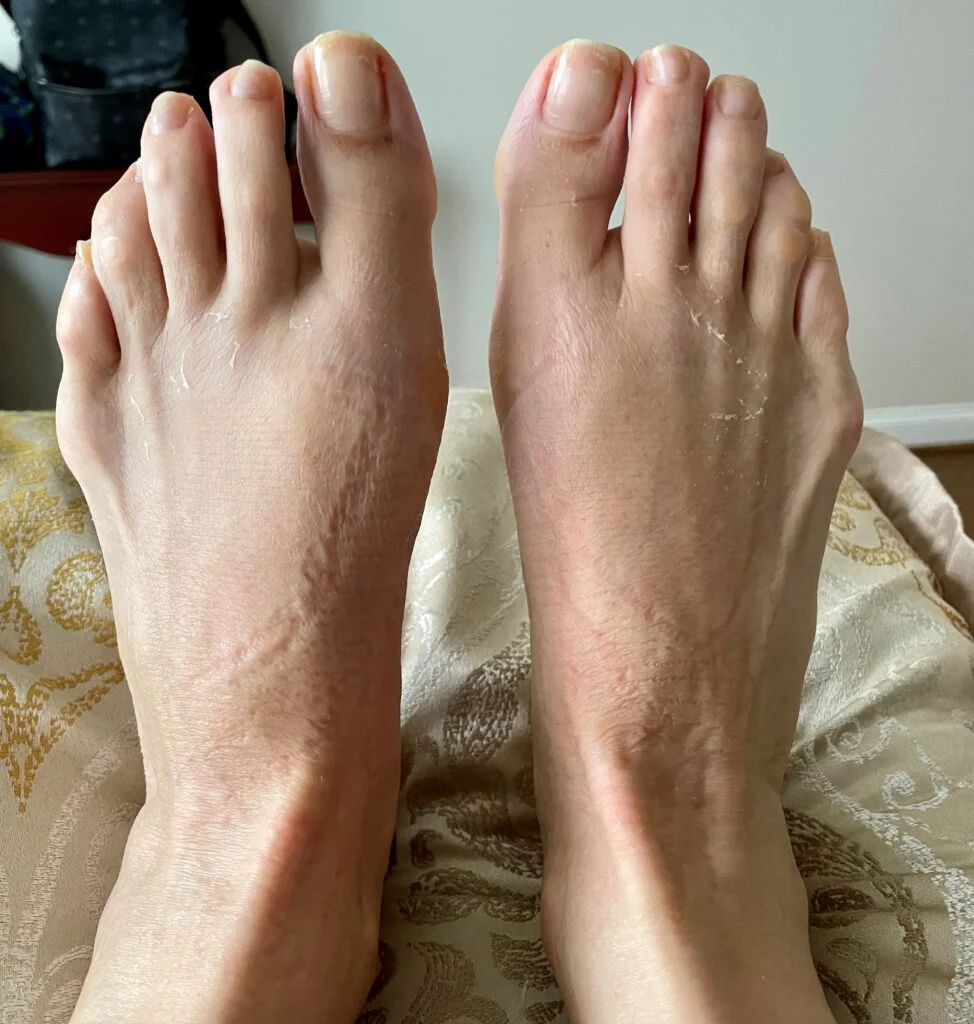
What Are The Signs And Symptoms of Bunions?
What Are The Risk Factors of Bunions?
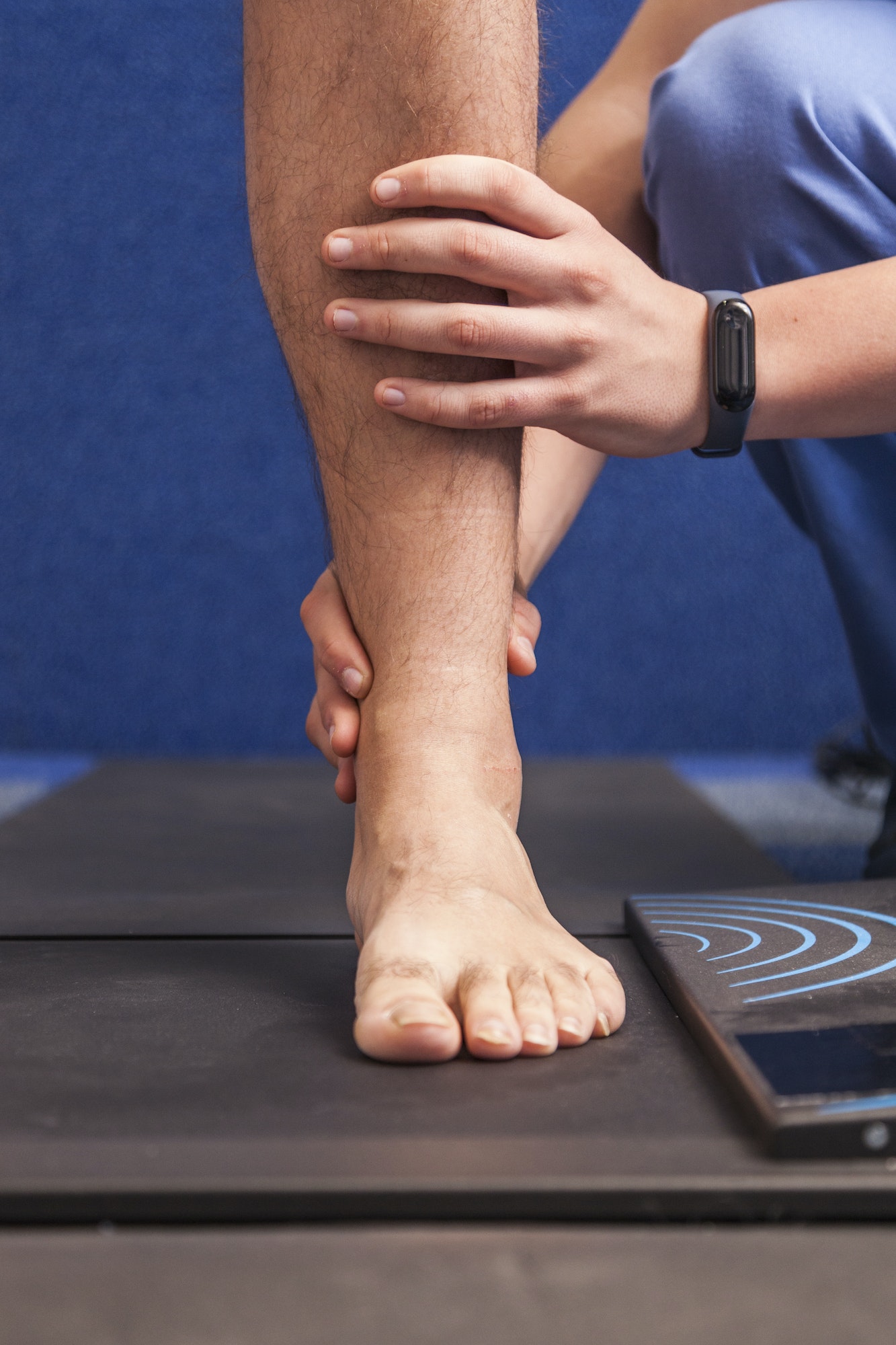
How Are Bunions Diagnosed?
What Are Possible Treatments For Bunions?
Conservative treatments for bunions can include wider and more supportive shoes, orthotics, foot pads, and anti-inflammatory medication. If you have a bunion, you should avoid shoes that are too small and narrow, high heels and shoes that are pointed at the toes. These methods can offer pain relief and slow down bunion formation, but will not correct the structural position of the toe joint.
In situations where a change in footwear is not enough to provide relief, surgical correction may be necessary. Should our podiatrists find that surgical treatment is the best course of action, there are a number of surgical procedures which have been developed to effectively treat bunions and restore the toe joint to a more aligned position.
Weil Foot & Ankle Institute proudly offers two proprietary procedures for treating bunions. These are:
- Lapiplasty: Addresses the instability by fusing a joint in the midfoot.
- Scarfplasty: Also known as the “Scarf Procedure,” this surgery was developed by the surgeons at Weil Foot & Ankle Institute and is now utilized worldwide. Scarfplasty aligns the bones and allows for a shorter recovery time than most bunion procedures. Both feet can be treated in a single surgery and patients can bear weight almost immediately after.
Surgical procedures for bunion removal are usually performed in the outpatient setting, either in a surgical center or hospital. In many cases, other associated conditions such as hammer toes may be corrected at the same time.
Are There Preventative Steps or Measures To Avoid Bunions?
What Are The Risks If Bunions Are Left Untreated?
As a bunion further progresses, the big toe will drift towards the lesser toes often underlapping the second and third toe. As the second and third toe are pushed upwards, these toes can begin to develop a hammer digit deformity. Changing the alignment of the toes can also cause arthritic changes to develop over time.
There are times where a fluid-filled cyst, or bursal sac, will grow between the skin and the joint overlying the bump. This can cause increased pain and a burning sensation.
Bunions often make wearing shoes very uncomfortable due to the increased width of the foot. Improper foot function and instability caused by a bunion can result in an uneven distribution of pressure, causing pain and possible callus formation to the ball of the foot.
Are There Other Related Conditions To Bunions?
Research & Publications On Bunions
View research and publications from Weil Foot & Ankle Institute on bunion surgery:
- Retrospective Comparison of Patients Undergoing Formal Physical Therapy Versus No Physical Therapy Following Bunion Correction
- Scarf Osteotomy for the Correction of Adolescent Hallux Valgus
(Foot & Ankle Specialist, February 2010) - Unilateral Versus Bilateral First Ray Surgery
(Foot & Ankle Specialist, June 2009) - Predicting articular erosion in hallux valgus: clinical, radiographic, and intraoperative analysis
(Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, January/February 2005) - Mastering The Scarf Bunionectomy
(Podiatry Today, January 2003) - ACFAS Universal Foot and Ankle Scoring System: First Metatarsophalangeal Joint and First Ray (module 1)
(Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, January/February 2002) - Scarf osteotomy for correction of hallux valgus. Historical perspective, surgical technique, and results
(Foot and Ankle Clinics, September 2000) - Bipartite tibial sesamoid and hallux abducto valgus deformity: a previously unreported correlation
(Journal of Foot Surgery, March/April 1992) - Hallux abductus interphalangeus. Etiology, x-ray evaluation and treatment
(Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association, February 1992)

Meet Weil Foot & Ankle Institute
By: Weil Foot & Ankle Institute, Published: May 20th, 2022
Review By: Lowell Weil Jr., DPM – Jan 19th, 2023